Rosacea Revealed: Delving into the How and Why Behind Its Symptoms
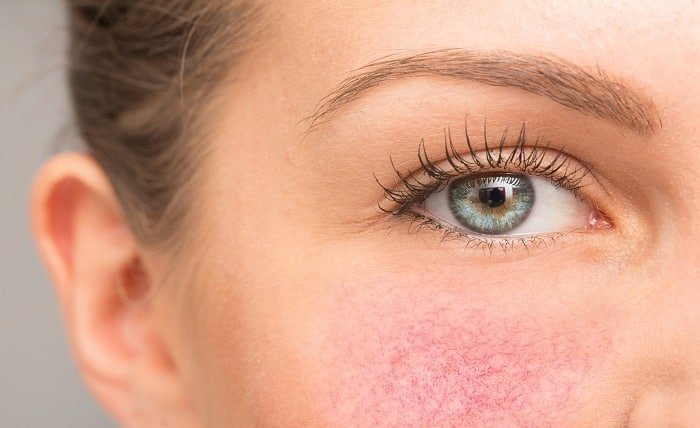
Rosacea is a prevalent and persistent skin condition impacting millions globally. Characterised by facial redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes small, red, pus-filled bumps, rosacea can be frustrating and embarrassing for those who experience it. This article will explore the underlying factors contributing to rosacea and the mechanisms behind its symptoms.
Although the precise origin of rosacea remains elusive, researchers have pinpointed numerous potential triggers and contributing elements. These encompass genetic predisposition, environmental influences, and immune system irregularities. Understanding these factors is critical for developing effective treatment strategies, including using rosacea cream and assisting individuals in managing their symptoms more effectively.
What is Rosacea?
Rosacea is a multifactorial condition arising from genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Though the cause of rosacea remains uncertain, researchers have recognised various potential triggers and contributing elements. These triggers and factors may vary from person to person, making rosacea a complex and individualised condition. Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, with family history often influencing susceptibility to rosacea. Environmental factors, such as exposure to sunlight, extreme temperatures, and specific dietary choices, can worsen symptoms or provoke flare-ups.
Additionally, immune system dysfunction is believed to contribute to the inflammatory response seen in rosacea, further complicating its pathogenesis. Understanding the interaction of these factors enables healthcare professionals to customise treatment plans, addressing each individual’s specific requirements and effectively alleviating their rosacea symptoms. Utilising rosacea creams formulated with soothing and anti-inflammatory ingredients can provide targeted relief and support overall skin health.
Genetic Predisposition
Evidence indicates that genetics contribute to rosacea development. Those with a family history of the condition are more likely to develop it themselves, highlighting a genetic predisposition.
Environmental Triggers
Certain environmental factors can exacerbate rosacea symptoms or trigger flare-ups. These triggers vary from person to person but may include sun exposure, hot or cold weather, wind, humidity, stress, spicy foods, alcohol, and certain skincare products.
Immune System Dysfunction
Some researchers believe rosacea may involve immune system dysfunction, leading to inflammation and skin dilation. This immune response can contribute to rosacea’s characteristic redness and flushing.
Mechanisms Behind Rosacea Symptoms
The exact mechanisms underlying rosacea symptoms are complex and not fully understood. However, several key factors are believed to contribute to the development of common rosacea symptoms, including:
Dermal Inflammation: Inflammation plays a central role in rosacea, contributing to redness, swelling, and irritation in affected areas of the skin. Chronic inflammation can lead to the dilation of blood vessels, resulting in persistent redness and visible blood vessels characteristic of rosacea.
Vascular Dysfunction: Another hallmark of rosacea is dysfunction of the blood vessels in the skin. Abnormalities in blood vessel structure and function can boost blood flow to the skin, leading to flushing and redness.
Neurovascular Dysregulation: Neurovascular dysregulation refers to the abnormal communication between nerves and blood vessels in the skin. In rosacea, this dysregulation can lead to excessive blood vessel dilation in response to specific triggers, such as heat, stress, or spicy foods.
Treatment and Management of Rosacea
Although there is no cure for rosacea, numerous treatment options exist to assist in symptom management and improve the overall outlook of the skin. These treatments may include:
Topical Therapies: Topical creams and gels containing ingredients such as azelaic acid, metronidazole, or ivermectin can help reduce the inflammation and redness of rosacea.
Oral Medications: Oral medications, including antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs, may be prescribed in certain instances to manage rosacea symptoms, particularly in cases of moderate to severe rosacea.
Lifestyle Modifications: Making specific lifestyle adjustments can also help manage rosacea symptoms. These adjustments may involve avoiding recognised triggers, shielding the skin from sunlight, and embracing a mild skincare regimen.
Laser and Light Therapies: Laser and light-based therapies can effectively target blood vessels and reduce the redness associated with rosacea. These treatments selectively heat blood vessels in the skin, prompting them to contract and diminish gradually.
Conclusion
Rosacea is a complex and multifaceted condition that can significantly impact the quality of life. With a comprehension of the underlying factors that contribute to rosacea and the mechanisms driving its symptoms, individuals can proactively take steps to manage their condition effectively. These strategies can effectively manage rosacea symptoms and promote skin wellness. However, by gaining insight into the underlying factors driving rosacea and the mechanisms behind its symptoms, individuals can empower themselves to confront the condition head-on. Individuals can regain control over their skin health and overall well-being through a comprehensive approach encompassing medical treatments and lifestyle adjustments. With perseverance and dedication to a tailored management plan, it is possible to navigate the complexities of rosacea and achieve a more comfortable, confident existence.